Pharmaceutical
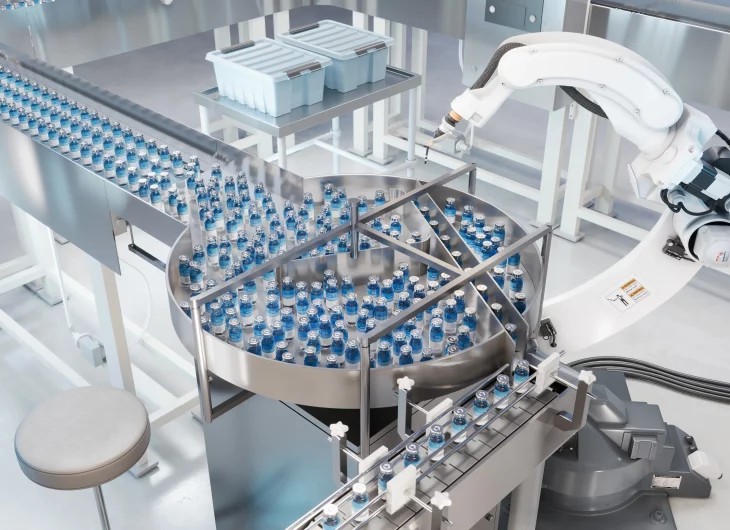
Robotic islands play a crucial role in the pharmaceutical industry, automating many of the operations to ensure the safety and efficacy of pharmaceuticals and medical products.
The main uses of robots and robot islands in the pharmaceutical and medical sector are as follows:
Dosing and filling
Robotic islands are used to precisely dose active ingredients and filling materials in pharmaceutical containers such as bottles, ampoules, blisters and syringes, This is because the robots ensure precise dosing, minimising waste and reducing the risk of contamination.
Sterile Packaging and packing
Robotic islands, robots and cobots are used to pack pharmaceuticals in sterile environments, ensuring that they are not contaminated; for example, in the packaging of pre-filled syringes, bottles, blisters, and medical devices.
Quality and Regulatory Compliance Inspection
The robot islands are equipped with advanced vision systems and sensors to visually inspect pharmaceutical products and ensure that they meet quality standards. There are significant advantages for inspecting vials, blisters, tablets and bottles to detect defects such as contamination, cracks, incorrect labels, or incorrect dosages.
Handling of Chemical and Biological Substances
These islands and robots are used for the safe handling of developing chemicals, biological substances and drugs, reducing the risk of exposure to operators. Ideal for mixing, liquid transfer, toxic dust management, and cell culture handling.
Traceability and Serialization
Robotised islands can be integrated with traceability and serialisation systems, which are essential to combat falsification of medicines and ensure the security of the supply chain, for example by applying bar codes, serial numbers and RFID tags on pharmaceutical packaging.
Automation in R & D laboratories
R&D laboratories use robots and cobots in well-defined areas to automate sample preparation, high-capacity screening tests, and the handling of sensitive materials. Crucial for chemical screening, gene sequence analysis, and sample preparation for mass spectrometry.
The pharmaceutical industry is one of the most regulated fields, where precision, quality, and regulatory compliance are the key.