Automotive
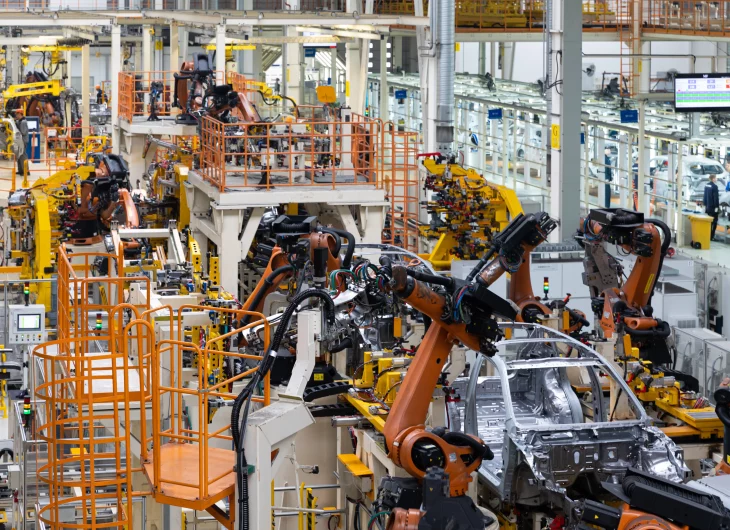
The main uses of robot islands in the automotive industry are:
Assembly of components
Assembly of components such as engines, transmissions, suspensions, and interiors. The most widely used technologies for these activities are assembly robots, automatic screwdrivers, and vision systems.
Welding of bodies
Robots are essential for welding body panels, joining metal parts with extreme precision, using spot welding, wire welding, TIG/MIG, and laser.
Painting
In the automotive sector, robotic paint islands ensure uniform application of colour and protective coatings on car surfaces. Robots with paint guns are used, inside sealed paint booths, with ventilation systems for overspray control.
Materials and Component Handling
In this case, robots are used to move heavy or delicate parts such as frames, motors and glass along the production line, reducing the risk of damage and speeding up processes, resulting in increased safety, reduced operator fatigue, improving the efficiency of the production line.
Quality control
Quality control robotic islands inspect components and finished cars to ensure they meet the high standards required by the automotive industry. They do this by using machine vision systems, 3D measurement sensors, and laser scanners.
Assembly of internal parts
Robots assemble internal parts such as dashboards, door panels and infotainment systems, ensuring precise and consistent assembly, use pressure sensors to prevent damage and have high accuracy in assembly.
Tyre Assembly
Automated tyre installation on wheels is another process where robot islands are widely used, thanks to robots with tyre grippers and positioning sensors.
Palletizing and Packaging
Once assembly is complete, the components or entire vehicles are packed and palletized for shipment, an operation that can be automated with robotic islands, using robots for handling, automated packaging systems, weight and dimension sensors.
Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing
Robot islands can also be integrated with 3D printing technologies for the production of custom components or prototypes, equipping robots with 3D printing and post-process handling technologies.
CNC machining
In the production of metal and plastic components, robot-operated islands work closely with CNC machines to perform operations such as milling, turning, and drilling. Collaborative robots (cobots), force sensors, human-machine interfaces (HMI) are often used.
The automotive sector is one of the main users of robotic islands and, in general, automation systems because it has always had the need to assemble vehicles with high precision, efficiency, and large volumes.